Gateway, Router, Modem, Switch and Hub
Published:
Many people may confused with these concepts, here I would like to make a easy-understanding interpretation of each.
Hub and Switch
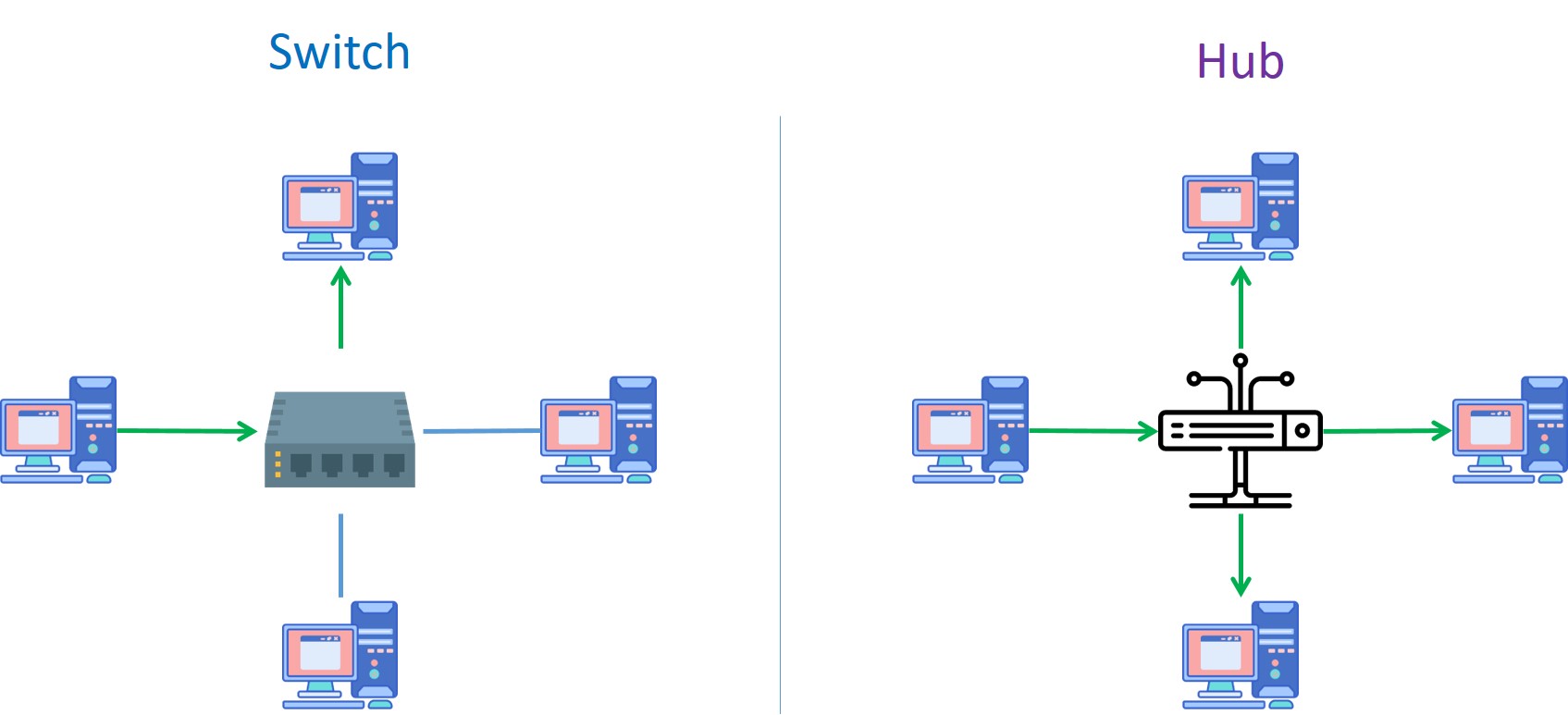 Each device connects one port of the hub. When one device sends data to the hub, the hub will transfer the data to all of other connected devices.
Each device connects one port of the hub. When one device sends data to the hub, the hub will transfer the data to all of other connected devices.
Compared to the hub, in switch the data will be directed only to intended port, this based on the MAC address of each device.
Switches and Hubs are used to exchange data with a Local Area Network (LAN). They cannot be used to exchange data outside their own network. To exchange data outside their own network, a device needs to be able to read IP addresses. Here we need Router.
Router
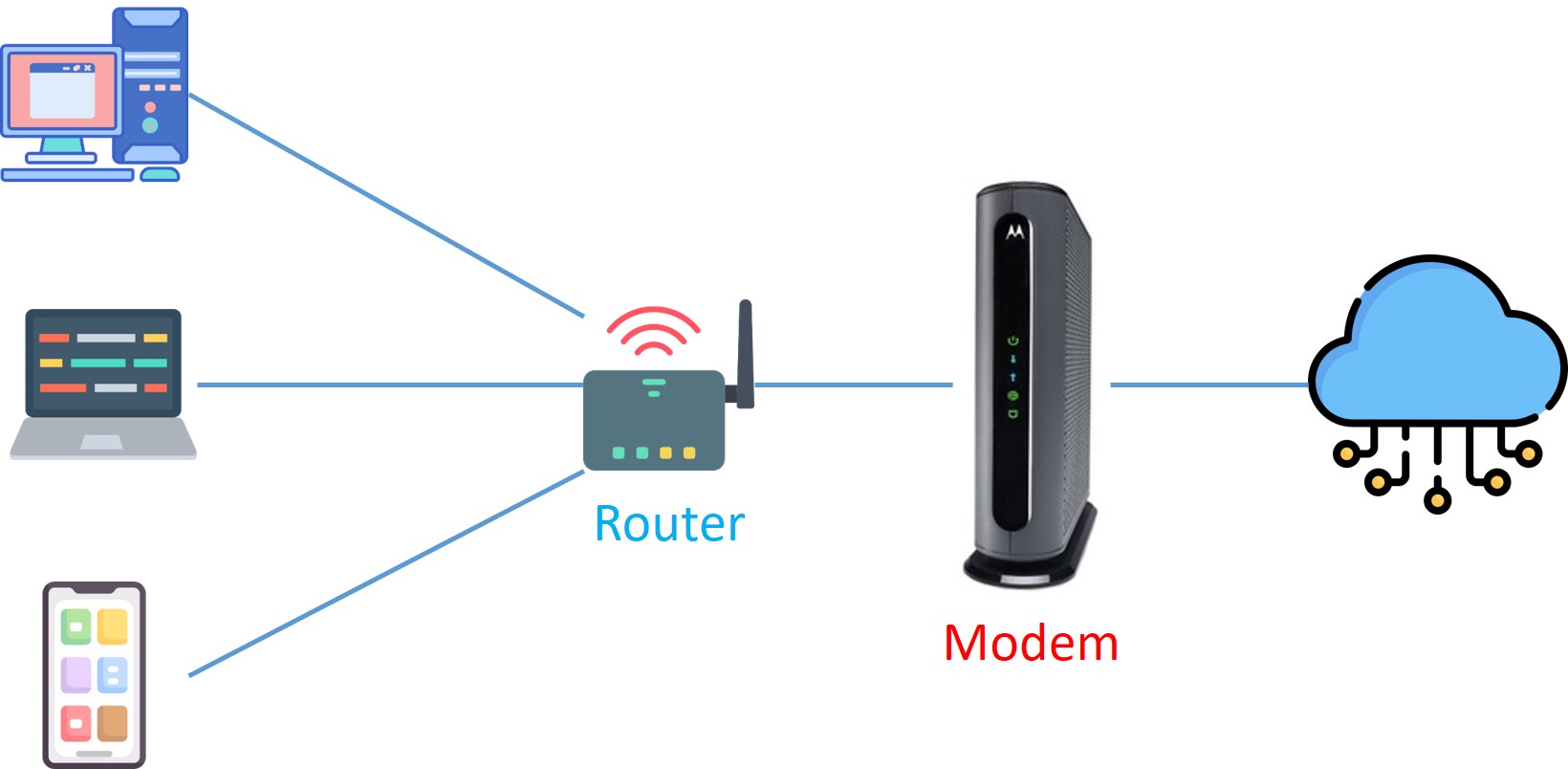 The router routes data from one network to another based on their IP address. When a data packet is received from the router, the router inspects the data’s IP address and determines if the packet was meant for its own network or if it’s meant for another network. So, a router is essentially the gateway of a network.
The router routes data from one network to another based on their IP address. When a data packet is received from the router, the router inspects the data’s IP address and determines if the packet was meant for its own network or if it’s meant for another network. So, a router is essentially the gateway of a network.
Gateway
Gateway also forwords data packets between networks, but where some conversion is required because the networks are running different, incompatible protocals.
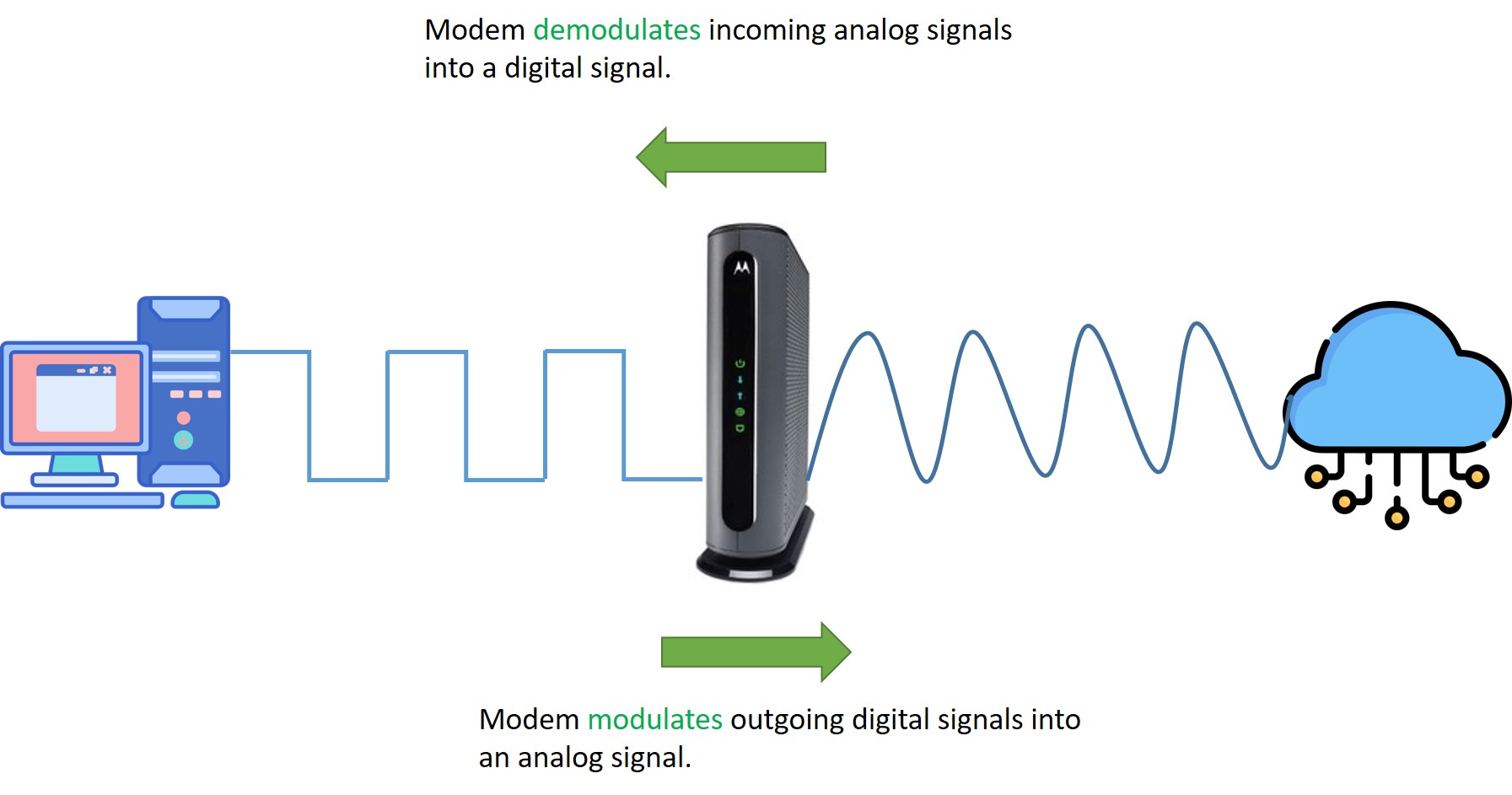
Modem
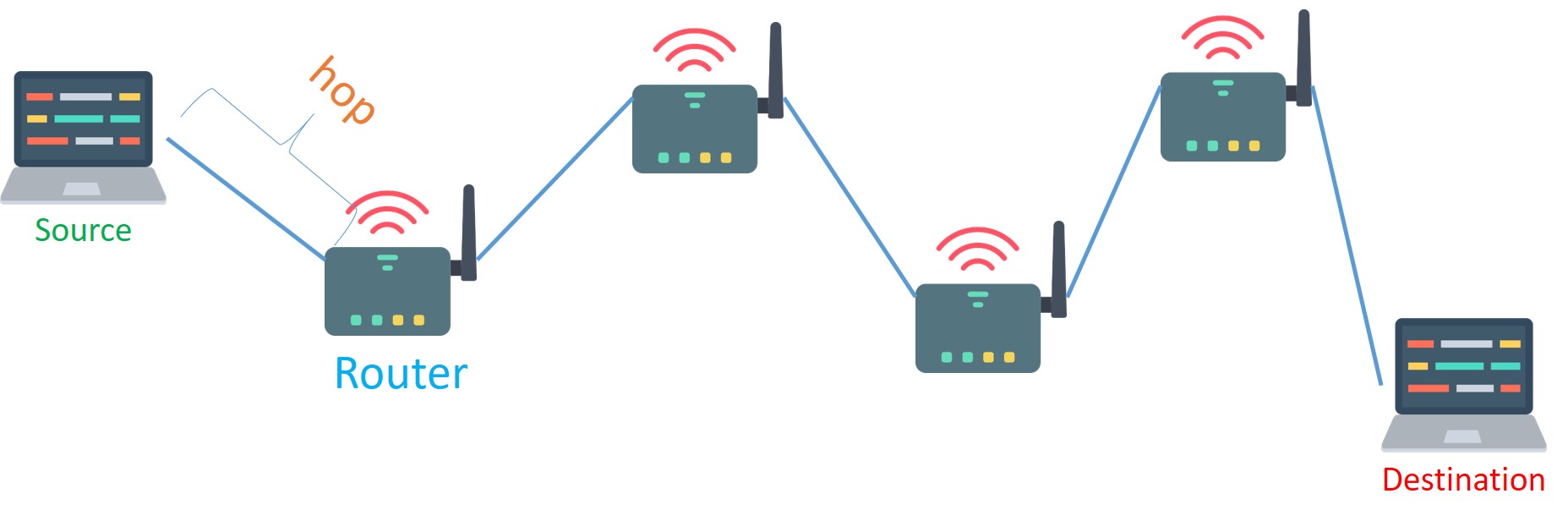
Single hop and multi hop
A hop means number of different networks a packet has to go through in order to reach its final destination address. In other word, a hop is the term for the jump from one router to another.
The main difference between single & multi-hop network is the number of hops a packet takes to reach the final destination .
Single hop network :
In a single hop network , when a packet leaves the source it just takes a single hop (goes through another network or you can say it passes through another router from a different network) before reaching its destination address.
Multi-hop network :
In a multi-hop network a packet has to go through two or more networks in order to reach its destination address.
Bandwidth
Definition: The maximum amount of data transmitted over an internet connection in a given amount of time.
Unit: Megabits per second (Mbps)
Megabytes per second (MB/s)
Conversion: K = kilo = 1000 bits
M = mage = 1000 kilo
G = giga = 1000 mega
T = tera = 1000 giga
1 byte = 8 bits, so 10 MB/s = 80 Mbps
